

Raw data would be difficult to analyze, and trend and pattern determination may be challenging to perform. It allows for data to be presented in a meaningful and understandable way, which, in turn, allows for a simplified interpretation of the data set in question. The variance reflects the degree of the spread and is essentially an average of the squared deviations.įor a deeper understanding of different foundational statistics concepts and tools, check out CFI’s Statistics Fundamentals course! Importance of Descriptive Statisticsĭescriptive statistics allow for the ease of data visualization. The standard deviation is used to determine the average variance in a set of data and provide an insight into the distance or difference between a value in a data set and the mean value of the same data set. The range depicts the degree of dispersion or an ideal of the distance between the highest and lowest values within a data set. The measures of variability determine how far apart the data points appear to fall from the center.ĭispersion, spread, and variability all refer to and denote the range and width of the distribution of values in a data set. The range, standard deviation, and variance are used, respectively, to depict different components and aspects of the spread. VariabilityĪ measure of variability is a summary statistic reflecting the degree of dispersion in a sample. The mode refers to the score or value that is most frequent in a data set. The median refers to the middle score for a data set in ascending order.
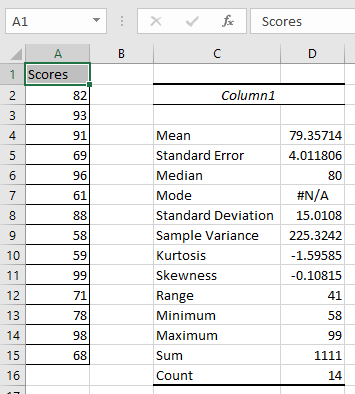
The mean, considered the most popular measure of central tendency, is the average or most common value in a data set. The mean, median, and mode are the measures of central tendency. Measures of central tendency are also known as measures of central location. Central TendencyĬentral tendency refers to a dataset’s descriptive summary using a single value reflecting the center of the data distribution. It allows for a more structured and organized way to present raw data.Ĭommon charts and graphs used in frequency distribution presentation and visualization include bar charts, histograms, pie charts, and line charts. Each entry in the table or graph is accompanied by the count or frequency of the values’ occurrences in an interval, range, or specific group.įrequency distribution is basically a presentation or summary of grouped data categorized based on mutually exclusive classes and the number of occurrences in each respective class. The frequency distribution is normally presented in a table or a graph. Used for both quantitative and qualitative data, frequency distribution depicts the frequency or count of the different outcomes in a data set or sample. Understanding the Different Types of Descriptive Statistics Frequency Distribution Descriptive statistics helps facilitate data visualization.Descriptive statistics comprises three main categories – Frequency Distribution, Measures of Central Tendency, and Measures of Variability.The term “descriptive statistics” refers to the analysis, summary, and presentation of findings related to a data set derived from a sample or entire population.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
